Lesson 8Check the datas! Why inclusive project management matters ?
- Notion 52 - What are the risks in the digital environment ?
- Notion 53 - What are testimonies of inclusion in the digital environement ?
- Notion 54 - Datas about women in the digital field
- Notion 55 - Datas about disability in the digital field
- Notion 56 - Datas about diversity in the digital field
- Notion 57 - Review of the main concepts
Notion 52
What are the risks in the digital environment ?
Target skills
Introduction to the digital divide
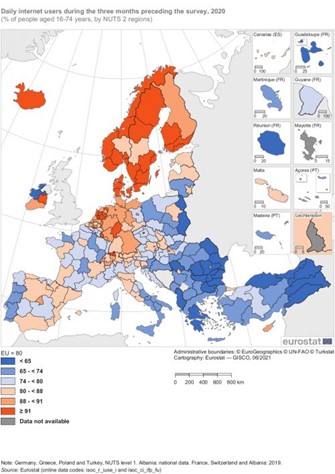
The graphic above shows the digital society statistics at regional level in Europe. It shows the percentage of daily internet users in every region of the European countries. We can see that Nothern Europe is the most connected area with more than 91% of internet users in most of the Scandinavian countries and more than 88% almost everywhere in Germany. France, Spain and Italy are a little more heterogeneous with 65 to 88% of daily internet users. This figures varies accross regions. Eastern Europe is the less connected area, with many regions having less then 65% of daily internet users.
To go further, you can visit the « Eurostat » category of the website ec.europa.eu.
Have you ever heard of the digital divide? This term describes inequalities of access, use and impact of information and communication technologies. Generally, it describes two very present inequalities: inequality in access to ICTs and inequality in their use. These inequalities are the main risk factors of exclusion in digital environments. As a digital manager, it is crucial to take these inequalities into account, whether it is towards your audiences, customers or employees.
Digital divide and access inequalities
Economic, social and territorial inequalities can be linked to inequalities in access to IT equipment or infrastructure.
- Network coverage
Europe has put in place an action plan to optimize the coverage of fixed and mobile networks in the countries of the Union, but some areas, especially rural and peripheral, are still disadvantaged. Many homes do not have access to a quality connection. Remember that it is difficult to view videos or consult sites containing animations without a broadband connection.
- Digital equipment
The digital equipment of the population in Europe is very uneven for many reasons. Some people do not wish to equip themselves by choice or by lack of knowledge. There are people who are not able to equip themselves for economic or social reasons. We must also take into account users who are equipped with only one device (either a computer, a tablet or a smartphone) or a device of an earlier version. While a majority of online content is now responsive, not everything is optimized for all screen resolutions. Some users may experience degraded browsing experiences depending on the tool they are using. The same is true for some older equipment. If you don't want to update your equipment, or if your equipment is no longer able to be updated, it is possible that certain functionalities are no longer optimized, or even no longer accessible, making it obsolete.
- How to prevent the risk of exclusion in these cases
- Develop your website in responsive design by considering multiple screen sizes.
- Ensure compatibility and optimization of your product with as many operating systems, browsers and different versions as possible.
- When applicable, keep an alternative to the use of the digital product: materialized version, phone line, physical reception point...
- Propose an alternative to the creation of an account and identification by e-mail
- Propose a consultation of possible elements off-line
- Pay attention to the weight of online elements so that they are as light as possible and do not require a lot of bandwidth to be viewed.
Digital divide and use inequalities
Quality access to digital technologies is a first requirement, but it is still necessary to master its uses for a good appropriation.
- Illectronism
Illectronism corresponds to digital illiteracy, i.e. a lack of knowledge that does not allow to understand and fully use computer tools. This level of knowledge is extremely variable and heterogeneous within the population.
It is assumed that the new generations, born in the digital age, have an increased knowledge in this field, but this phenomenon of illiteracy affects all categories of the population.
- Lack of awareness
A lack of understanding of how digital tools work and a lack of awareness of their risks can also lead to biased or unwise use.
It is necessary to know and be aware of data protection, online advertising, fake news, addiction risks... And to be able to be critical and stand back from the information we are exposed to.
- Situation of disability
As you have seen in the previous module, people with disabilities can also have difficulties in accessing the digital world. To see or review the accessibility issues for people with disabilities, you can refer to this module, especially lessons 3, 4, 5 and 6 which will allow you to understand the different types of disabilities and their impact on the use of digital technology.
- How to prevent the risk of exclusion in these cases
- Put the user at the center of the design, based on his main need and by integrating him in the development process via interviews, user tests...
- Propose simple, sober layouts that respect universal development standards and repositories. You can refer to module O5 to review the principles of accessibility and universal design.
Sources :